About BPH
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is a common condition in men as they age. It refers to the non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland, which can lead to urinary symptoms that affect your daily life.
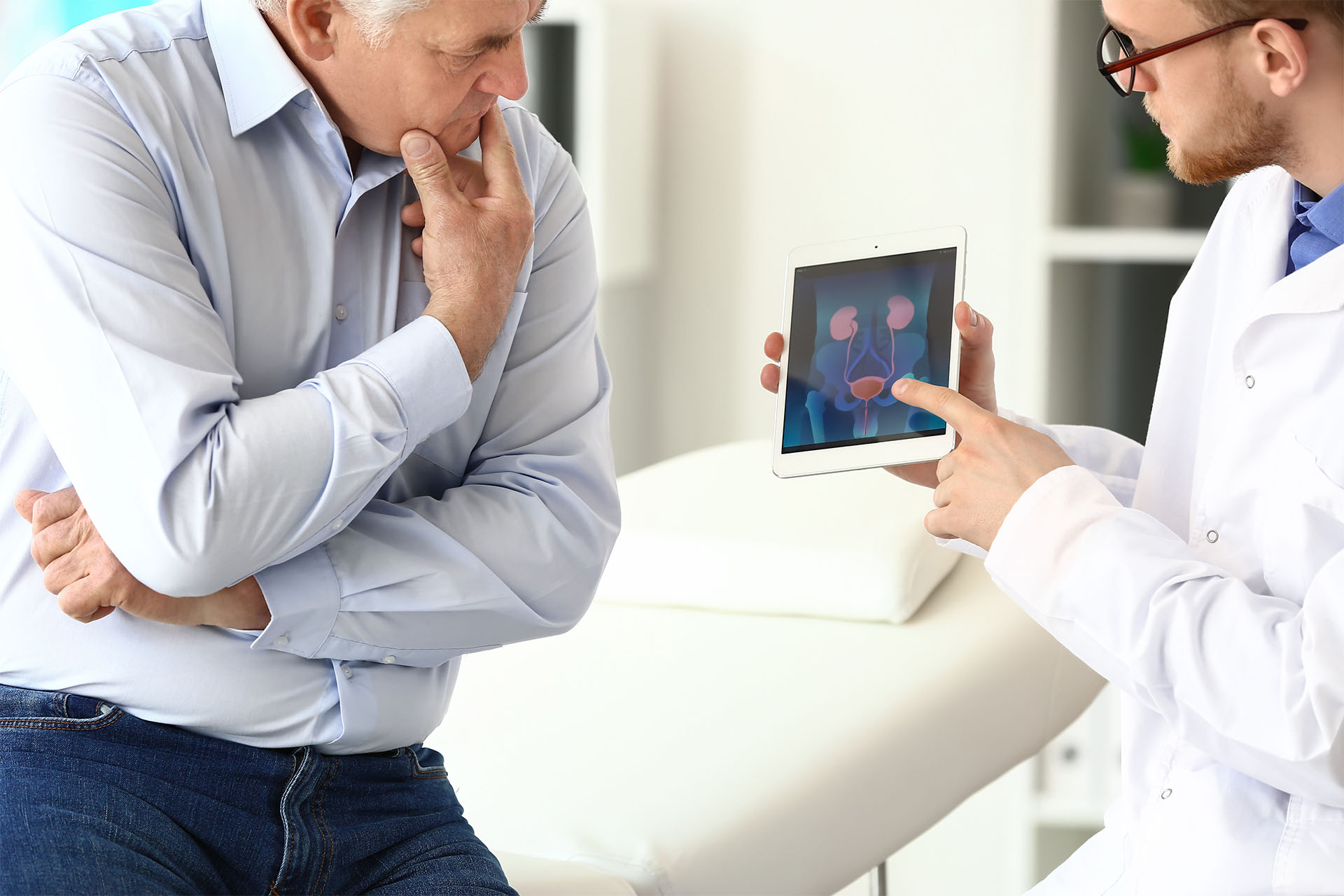
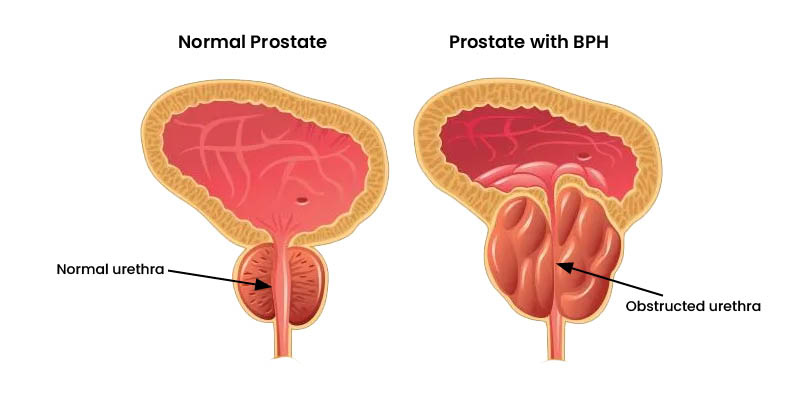
The prostate is a small, walnut-shaped gland located just below the bladder and in front of the rectum. Its primary role is to produce fluid that nourishes and transports sperm. As men get older, the prostate can grow larger, which may press against the tube that carries urine out of the body, making it harder to urinate.
“Whilst its not generally considered life threatening, BPH can significantly impact your quality of life. In fact, it’s one of the fastest growing diseases causing years lived with disability and in the last 20 years the prevalence has increased dramatically.”
Dr Thayne Larson
Take the BPH Symptom Assessment
The American Urological Association (AUA) Symptom Score is a widely used questionnaire designed to help assess the severity of urinary symptoms related to BPH. It provides a simple and standardised way for patients and healthcare providers to measure how BPH is impacting daily life.
The questionnaire includes seven questions about common urinary symptoms. Each question is scored on a scale from 0 (not at all) to 5 (almost always). The total score helps categorise symptom severity as mild, moderate, or severe, and will help your doctor find the best treatment for you. In addition, the AUA Symptom Score includes a question about how bothered you feel by your symptoms, allowing for a more personalised approach to care.
How ProstaCare is helping:
Current Treatment Options
There are may options available for treating your BPH and it's important to work with your health practitioner to find the right one for you. If left untreated BPH can lead to complications that may significantly impact your health and quality of life (careful as 'watch and wait' is an accepted option). As the Prostate continues to enlarge, it can place increasing pressure on the bladder and urethra potentially causing urinary retention, bladder stones, bladder or kidney damage and urinary tract infections.